Unlocking the Future: The Rise of Quadruped Robots
Quadruped robots are autonomous mobile machines that walk on four legs, imitating the gait and balance of animals such as dogs, horses, or big cats. Unlike traditional wheeled robots, they don’t rely on flat, even surfaces — instead, they can climb stairs, move across gravel, handle slopes, and navigate rough or cluttered environments with ease.
The line between science fiction and industrial reality is blurring faster than ever. Among the most striking examples of this technological evolution are quadruped robots — four-legged mechanical marvels that combine agility, stability, and artificial intelligence to navigate the physical world just like living creatures.
From industrial inspection and logistics to agriculture, security, and disaster response, quadruped robots are redefining what autonomous mobility can achieve. As global industries seek smarter, more resilient automation systems, these robots stand out as symbols of adaptability, precision, and engineering brilliance.
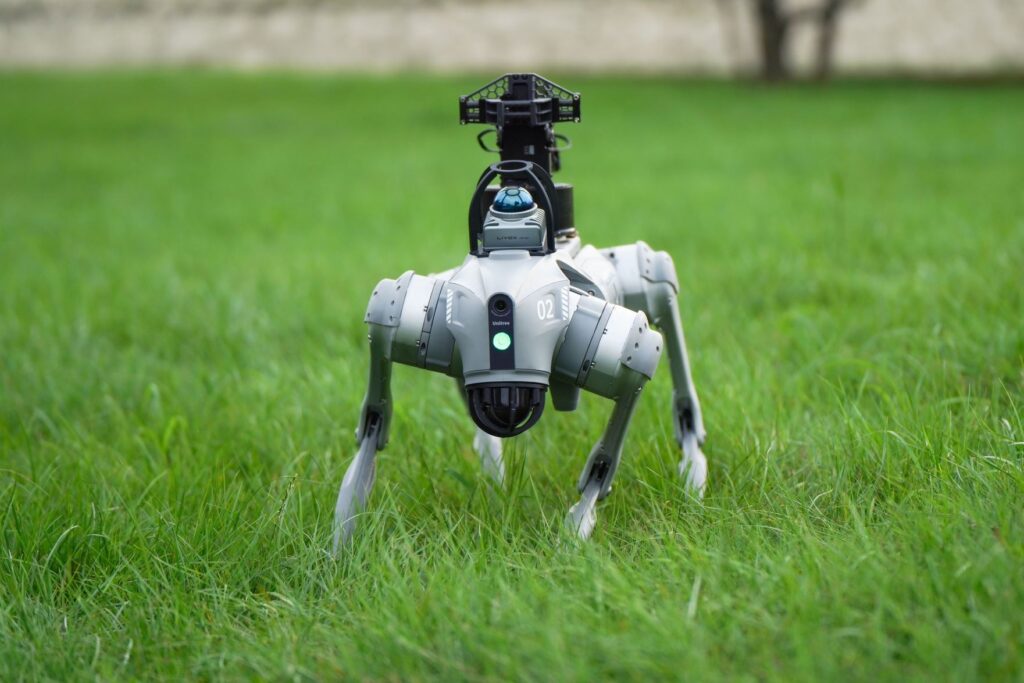

Anatomy of a Quadruped Robot
Understanding how a quadruped robot is built offers a glimpse into the intricate synergy between mechanical design, electronic intelligence, and artificial adaptability. Each component of the robot plays a vital role in creating the lifelike, stable, and fluid movement that makes these machines stand out in modern robotics.
Body Frame – The Structural Core
The body frame serves as the central skeleton of the quadruped robot, providing both strength and balance. It houses core components such as batteries, onboard computers, processors, and communication modules.
Built from lightweight yet durable materials like aluminum alloys, carbon fiber, or high-density polymers, the frame ensures optimal weight distribution. This allows the robot to remain stable during dynamic movements, sudden turns, or climbs.
Leg Assembly – The Engine of Motion
Each of the robot’s four legs is a marvel of mechanical precision. They are composed of hip, knee, and ankle joints, connected by articulated segments that move through a coordinated range of motion.
These joints are powered by servo motors or hydraulic actuators that replicate the muscular movement of animals. Servo motors offer speed and precision, while hydraulic systems deliver the raw power needed for heavy lifting or navigating rough terrain.
Sensors – The Eyes and Ears of the Robot
A quadruped’s intelligence begins with its sensory perception. The robot is equipped with a network of vision cameras, LIDAR sensors, depth sensors, gyroscopes, IMUs (Inertial Measurement Units), and tactile sensors.
These sensors continuously collect data about the robot’s surroundings — including surface texture, inclination, distance to obstacles, and environmental lighting. This sensory input allows the robot to map its environment in real time, recognize objects, detect hazards, and make micro-adjustments to its gait for optimal balance and performance.
Control Unit – The Brain Behind the Balance
At the heart of the system lies the control unit, an onboard computer that acts as the robot’s central nervous system.
It processes millions of calculations per second, using AI-driven algorithms to interpret sensor data, optimize gait cycles, and predict terrain challenges.
Through this control logic, the robot can adjust its posture, redistribute weight, and plan its next steps with remarkable precision.
Power System – The Energy Backbone
Powering this complex ecosystem is an advanced battery and energy management system. Most quadruped robots rely on high-density lithium-ion or lithium-polymer batteries, optimized for long runtime and consistent power delivery.
Some next-generation designs incorporate regenerative braking systems that recover energy during movement, extending operational time and improving efficiency.
How Quadruped Robots Work
At the heart of every quadruped robot is a complex ecosystem of hardware, software, and AI integration.
Perception Systems:
These include LIDAR sensors, depth cameras, ultrasonic sensors, and inertial measurement units (IMUs) that collect 3D data from the surrounding environment. The robot builds a live digital map to understand terrain, slope, and obstacles.Locomotion Control:
A powerful onboard processor runs real-time motion algorithms that calculate how each leg should move, balance weight distribution, and adjust speed. Some robots even switch between walking, trotting, and galloping gaits depending on terrain complexity.Artificial Intelligence:
AI plays a central role, enabling predictive movement and autonomous decision-making. It learns patterns over time — for instance, anticipating slippery surfaces or unstable ground — to move with human-like intuition.Power & Communication Systems:
Most quadrupeds use lithium-ion batteries for 1–2 hours of operation. They can be remotely controlled or programmed for fully autonomous missions using wireless networks and onboard AI navigation.
Together, these systems make quadruped robots remarkably self-sufficient, perceptive, and adaptable — capable of operating where traditional machinery cannot.
Key Features
| Parameter | Description / Data Point |
|---|---|
| Mobility Type | Four-legged locomotion mimicking animal gait |
| Average Speed | 1.5–3 m/s (depending on terrain and payload) |
| Payload Capacity | 10–40 kg (commercial); up to 120 kg (industrial/military) |
| Battery Life | 60–120 minutes per charge |
| Terrain Handling | Stairs, rubble, uneven ground, slopes, industrial sites |
| Key Sensors | LIDAR, IMU, depth cameras, ultrasonic, GPS, force sensors |
| AI Capabilities | Terrain mapping, obstacle avoidance, adaptive navigation |
| Global Leaders | Boston Dynamics (Spot), ANYbotics, Unitree Robotics, Ghost Robotics |
| India Use Cases | Plant inspection, surveillance, farm monitoring, logistics automation |
| Global Market Growth | CAGR of 24.3% projected (2024–2030) |
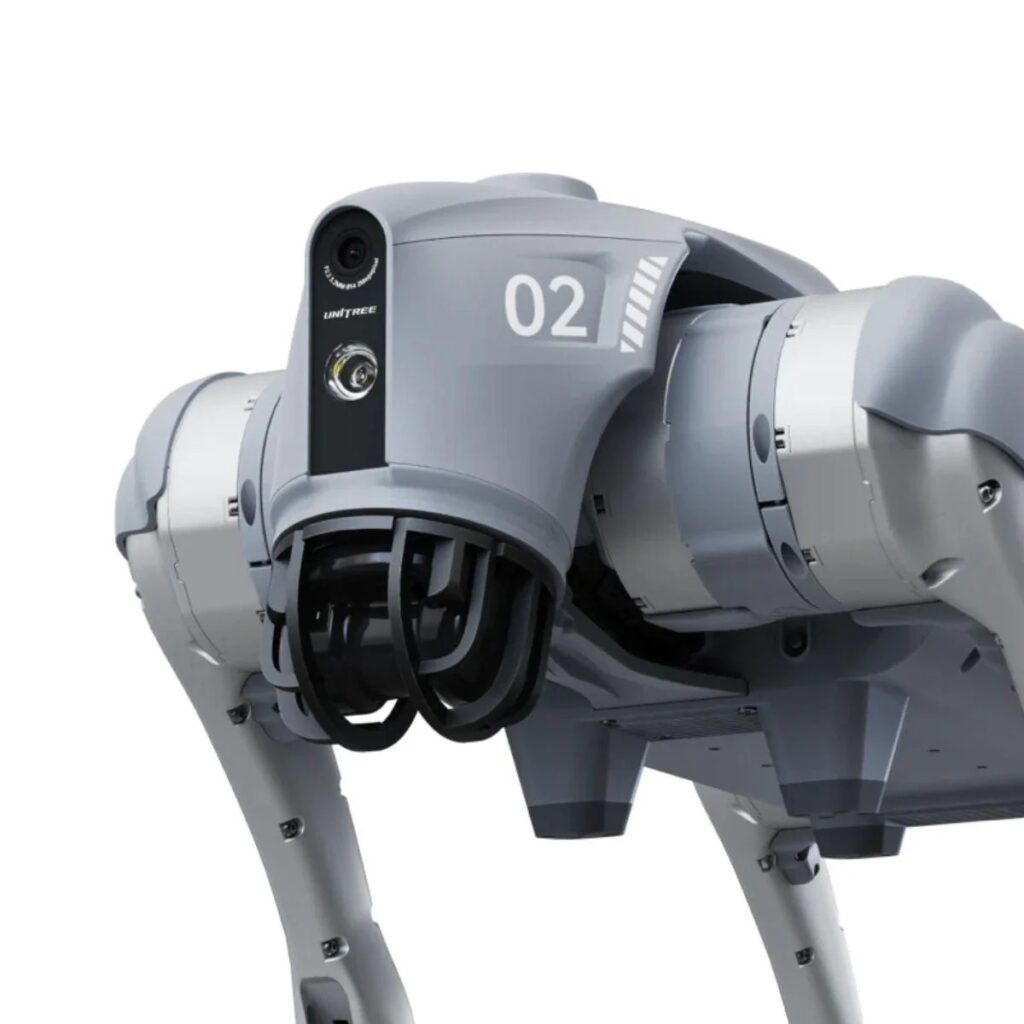

Advantages of Quadruped Robots
Quadruped robots bring together engineering sophistication and real-world versatility, making them indispensable across industries.
Autonomous Intelligence:
Modern quadrupeds come with vision-based AI systems that interpret surroundings, detect objects, and chart optimal routes — enabling fully autonomous operation.
Adaptability Across Environments:
They can work indoors, outdoors, on steep slopes, and in extreme temperatures. This flexibility allows deployment in industries.
Safety and Efficiency:
By taking over tasks that are too dangerous or physically demanding for humans, quadruped robots enhance workplace safety.
Together, these systems make quadruped robots remarkably self-sufficient, perceptive, and adaptable — capable of operating where traditional machinery cannot.
Why Quadruped Robots Are the Future
Quadruped robots represent a paradigm shift in how automation interacts with the physical world. They embody the evolution of robotics from rigid, pre-programmed machines to intelligent, adaptable partners capable of real-world decision-making.
Their ability to operate in unpredictable environments makes them indispensable for next-generation infrastructure, smart cities, and defense ecosystems. With governments, startups, and research institutions investing in robotics innovation, the demand for mobile, AI-powered systems like these will only grow.
For India, where industries often face terrain diversity, infrastructure challenges, and safety constraints, quadruped robots provide a scalable, intelligent solution for field automation and real-time monitoring.
Conclusion: The Four-Legged Leap Toward the Future
Quadruped robots symbolize humanity’s progress toward intelligent, terrain-adaptive automation. Their ability to move, sense, and decide with agility brings an unmatched advantage across industries that value precision, safety, and autonomy.
The future of robotics will walk — not roll — into new territories, driven by innovation, intelligence, and the steady steps of four-legged design.
Explore next-generation robotics and autonomous mobility solutions at Dronevex